hypertrophy is a biological concept that refers to the Enlargement of an organ or tissue from the increase in the size of its cells. In fitness, Muscle hypertrophy describes specifically An increase in muscle fiber sizeWhich leads to visible muscle growth.
It is a main goal for many athletes, bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts who want to improve aesthetics, strength and overall performance.
What is muscle hypertrophy?
Muscle hypertrophy is the adaptive reaction of muscle tissue to repeated resistance training. If you subdue your muscles of mechanical tensions, react by increasing them Cross -sectional area of muscle fibers.
This growth leads:
- Increased strength
- Improved metabolic function
- Improved physical
How does muscle hypertrophy occur?
Muscle hypertrophy is mainly triggered by Three key mechanisms (Schoenfeld, 2010):
- Mechanical tension:
Last-induced power on the muscle during the resistance exercises (e.g. squats, push-ups). - Muscle damage:
Micro-Tears from movement stimulate the repair and adaptation (the pain you feel). - Metabolic stress:
Accumulated by-products such as lactate during high rep or high volume training increase the cellular swelling and growth signals.
These mechanisms activate paths such as Mtor (Mammal destination by Rapamycin)which regulate Muscle protein synthesis (MPS)– The building block of hypertrophy.
Types of muscle hypertrophy
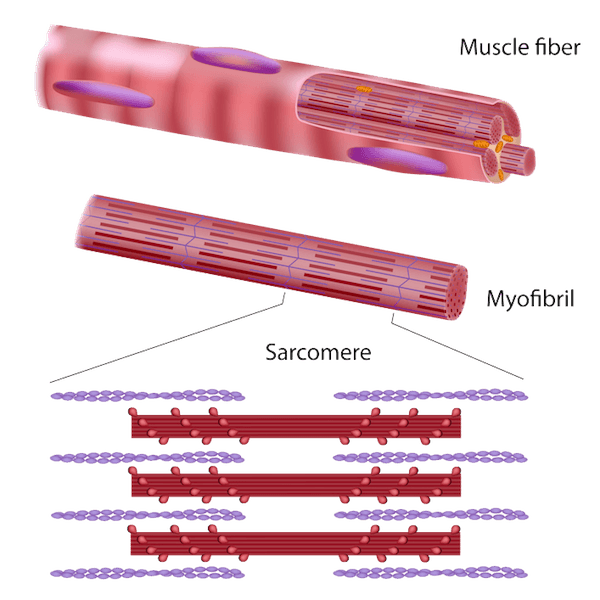
There are Two main types of hypertrophyEveryone reacts to different training stimuli:
1. Myofibrillary hypertrophy (functional hypertrophy)
An increase in size and number of myofibrils (contractile units of muscle fibers), which leads to denser, stronger muscles.
Characteristics:
- Reinforces the muscular strength and strength.
- Minimal increase in muscle size compared to sarcoplasmic hypertrophy.
- Improves power production and neuromuscular efficiency.
Training style:
- Heavy weights
- Lower repetitions (3–6)
- Longer calm (2–5 minutes)
- Focus: Composed elevators (e.g. squats, cross lifting, bench press)
2. Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy (non -functioning or size hypertrophy)
An increase in the volume of the sarcoplasmic liquid (non -contractile elements) within the muscle cell, which contributes to greater muscle size, but not necessarily greater strength.
Characteristics:
- Promotes muscle endurance and muscle size.
- Less improvement in maximum strength.
- Often in bodybuilding training.
Training style:
- Medium weight
- Higher repetitions (6–12+)
- Shorter calm (30–90 seconds)
- Focus: insulation exercises and volume (several sentences)
Bonus: transient hypertrophy
A temporary increase in muscle size during and immediately after training due to an increased blood flow (“the pump”).
Characteristics:
- Short -lived swelling of the muscles.
- Not with long -term size or strength gains.
- Can improve the linking of the thought muscles and the nutrient levy.
Summary table:
| type | Primary adjustment | Gain | Size profit | Training focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myofibrillary hypertrophy | Contractile proteins | High | Moderate | Low repetitions, heavy loads |
| Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy | Cell fluid/energy storage | Low | High | High repetitions, moderate loads |
| Transient hypertrophy | Blood flow/inflammation | None | Temporary | Pump training |
Do muscle hypertrophy influence?
Yes. Genetics play an important role To what extent someone can win muscle mass. Like: How:
- Muscle fiber: Fast-sugar fibers (type II) hypertrophy lighter than slowly twitching
- Hormoneller profile: Higher concentrations of testosterone and growth hormone prefer growth
- Satellite cells: Influence of muscle repair and growth
- Myostatin mirror: A genetic regulator that inhibits muscle growth (more on this below)
That means almost Everyone can build musclesEven if it is at different prices.
What is myostatin muscle hypertrophy?
Myostatin is a protein that limits muscle growth. People with Myostatin -Genmutations (either of course or through oppression) can experience Dramatic hypertrophyoften referred to as “Myostatin-related muscle hypertrophy.”
This condition is rare and can lead to people have Twice the normal muscle mass– even without extensive training. For most people, however, Myostatin remains an important controllerAnd training/nutrition must be optimized to build muscle in a natural way.
What should be done to increase muscle size and build muscle?
In order to promote muscle hypertrophy, you need a consistent and scientifically supported strategy that contains:
- Resistance training: Use connection and insulation exercises
- Progressive overload: Gradually increase the weight, repetitions or sentences
- Training up to close failure: The goal is 1–2 repetitions that have muscular failure
- Appropriate volume: 10–20 sets per muscle group per week
- Sufficient recovery: At least 48 hours between training the same muscle group
- Muscle -focused technology: Prioritize the tension and the shape of heavy weights
Normally, Bodybuilding workouts The aim is to concentrate on hypertrophy with these strategies.
How often should you train to achieve muscle hypertrophy?
Optimal frequency For hypertrophy, the training volume and individual recovery depends:
- Beginner: 3 days/week full body sessions
- Intermediate/advanced: 4–6 days/week, shared routines (e.g. Press/pull/legs)))
- Ideal frequency: Train every muscle group 2 times a week
This approach maximized Muscle protein synthesisWhat about 24–72 hours After training.
What are the best ways to make optimal use of your exercises for muscle hypertrophy?
- Use composite elevators (Hocke, cross lifting, bench press) for the total mass
- Add Isolation exercises For weaknesses (e.g. biceps, delts)
- Focus on Form and complete areas of movement
- Integrate Tempo training (Slow eccentric)
- Keep rest periods between the resting places 30–90 seconds For hypertrophy
- Use Drop sets, super sets and pyramids Increase metabolic stress
- Follow your progress weekly to ensure Progressive overload
How should you eat to build muscles?
Nutrition is half the battle in hypertrophy. Follow the following principles:
Macronutrients:
- Calories: Excess of ~ 250–500 kcal/day
- Protein: 1.6–2.2 g per kg body weight per day
- Carbohydrates: Fuel for training and restoration (3–5 g/kg)
- Fat: Essential for hormone production (0.8–1g/kg)
Timing:
- Eat 20–40 g protein every 3–4 hours
- Consume Carbohydrates + protein after training To support deputies
- Remain hydrated Support the recovery and cell volume
How do you increase muscle size? (Fast checklist)
✔ CONATED THE THE THE PROTECTIONS
✔ Use progressive overload strategies
✔ Beat every muscle twice/week
✔ Eat in a calorie surplus with sufficient protein
✔ Sleep 7-9 hours/night for recovery
✔ Manage stress and follow the results
What are the advantages of muscle hypertrophy?
- Improved strength and performance
- Higher metabolic rate (burn more calories in peace)
- Better bone density and joint support
- Increasing mood and cognitive function
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases (diabetes, heart disease)
- Improved appearance, trust and attitude
Diploma
The muscle hypertrophy is not only for bodybuilders, but a fundamental adaptation that almost every benefit. Regardless of whether you train for health, aesthetics or performance, you understand how muscles you grow, what influences you and how you can use the principles of hypertrophy to achieve your goals effectively.
Commit for the process, follow science and profits will come.
References
- Schönfeld, BJ (2010). The mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application for resistance training. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 24 (10), 2857–2872. Read the study
- Haun, CT, et al. (2019). Training volume and muscle hypertrophy: a systematic overview. Borders in physiology, 10, 447. Read the study
- McCall, GE, et al. (1999). Muscle fiber hypertrophy, hyperplasia and capillary density at College men after resistance training. Journal of Applied Physiology, 81 (5), 2004–2012. Read the study





