Starting a cardio routine in the gym can feel overwhelming. Rows of machines, flashing screens and unsafe steps can ask themselves: Which cardio equipment is best for me as a beginner?
The good news: You don’t have to master every machine. A couple Key pieces of Cardio devices Fame for the subsequent book of nakel, effectiveness and low risk of injury – and make them perfect for beginners.
In this guide we will explore the top 5 beginner-friendly cardio machines, how to use them correctly and which best suits your goals.
What does cardio device beginner-friendly?
Before you immerse yourself in the list, you must search for the following:
- Low learning curve (Simply operating without a trainer)
- Joint-friendly (Low effects on knees/hips)
- Adjustable intensity (Resistance/speed control)
- Comfortable attitude and step
- Suitable for all fitness levels
Top 5 best cardio machines for beginners
1.
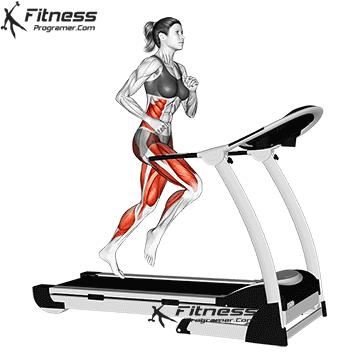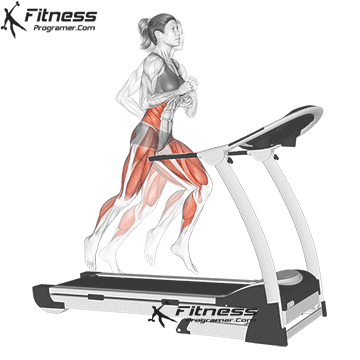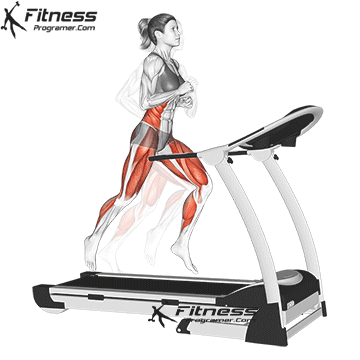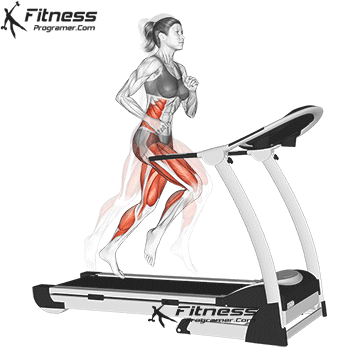
Best for: Go or jog
Muscles worked: Watch muscles, knee tendons, calves, core
The treadmill is one of the most popular and intuitive machines for beginners. You can start with a rapid walk and develop on walking or the light jogging.
Beginner tips:
- Start with a tendency of 0–2%to reduce the knee length
- Go at 2.5-3.5 miles per hour to an aerobic basi
- Use the safety clip and avoid leaning on handrails
Professionals:
- Natural movement pattern
- Easy to follow progress with distance, calories and speed
Disadvantages:
- Running can be high for some users
2. Elliptical trainer
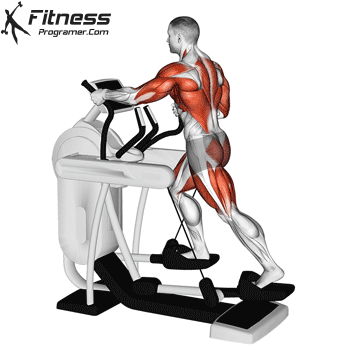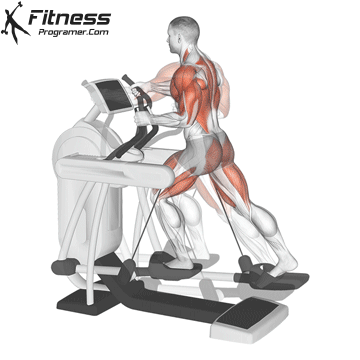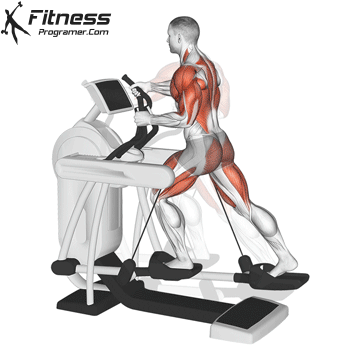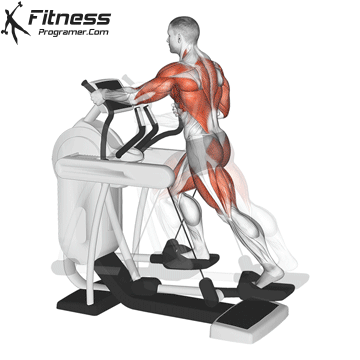
Best for: Low-impact, full body cardio
Muscles worked: Quads, knee tendons, gluteal muscles, chest, arms
Ellipticals offer a smooth, sliding movement that is easier for the joints than running ribbons. Most models have movable handles to activate the upper body and offer total body training.
Beginner tips:
- Concentrate on attitude – high with relaxed shoulders
- Use the level of resistance to check the intensity
- Start with 15 to 20 minutes with low resistance
Professionals:
- Ideal for common health
- Committed both the upper and the lower body
Disadvantages:
- The coordination needs some sessions to get used to it
3. Inpatient bike (upright or lying)
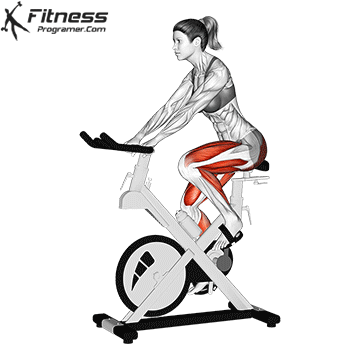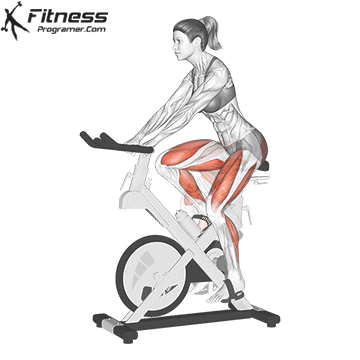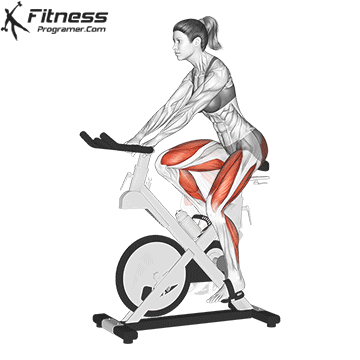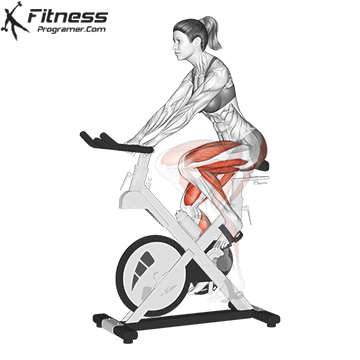
Best for: Sitting cardio with a minimal joint voltage
Muscles worked: Quads, gluteal muscles, calves
Inpatient bicycles are ideal for beginners, especially for those with joint pain or limited mobility. The Bike Offers back support while the upright bike Offers a more traditional bicycle posture.
Beginner tips:
- Set the seat height to align your knee at a 25–35 ° flexion on the bottom of the pedal stroke
- Start at a moderate pace at 10 to 15 minutes
Professionals:
- Low common effect
- Simply maintain consistent cadence
Disadvantages:
- Can be less appealing than other machines if it is done alone
4. Rowing machine (ergometer)
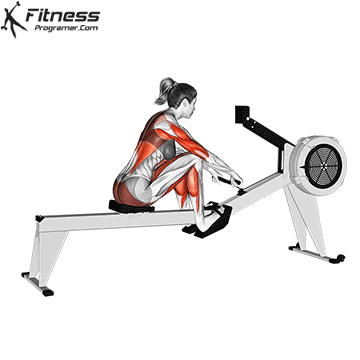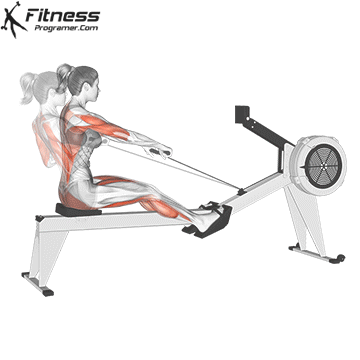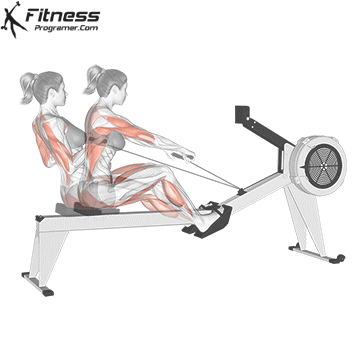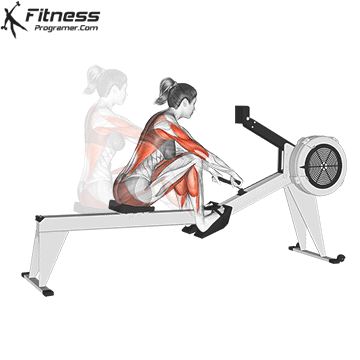
Best for: Full body conditioning, strength and posture training
Muscles worked: Back, shoulders, arms, legs, core
The rowers offer calorie -shaped training with little influence that builds up strength and endurance. Although it is a bit more technical, it is still a beginner with a short learning curve.
Beginner tips:
- Learn the stroke pattern: Legs → back → arms
- Keep your back straight – more hump
- Start with 3 to 5 minutes to the Übelechnik
Professionals:
- Full body activation
- Improves posture and cardiovascular fitness
Disadvantages:
- Requires coordination and technology for the best results
5. Stair climber (stairs stepper)
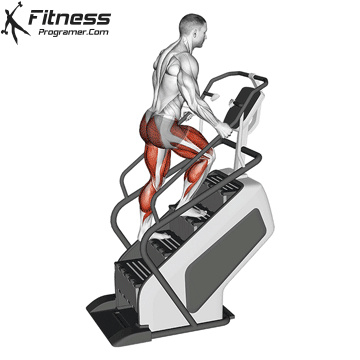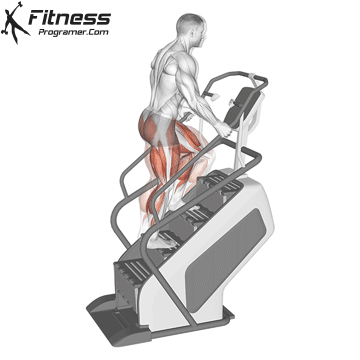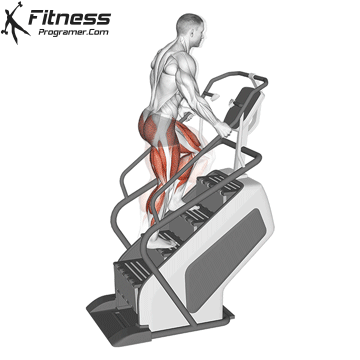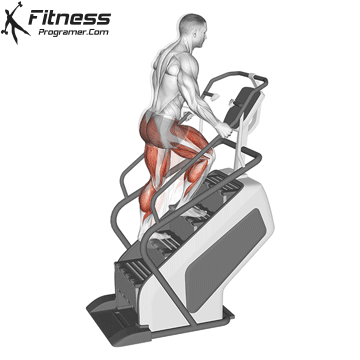
Best for: Endurance in the lower body and calorie fire
Muscles worked: Buttocks, calves, quads
This machine imitates stairs, a natural and highly effective movement to strengthen the legs and buttocks. It is ideal for short cardio burdens with high intensity.
Beginner tips:
- Start slowly – do not grab the rails
- Maintain upright attitude
- Try 1–2 minutes -intervals, followed by calm
Professionals:
- Ideal to tighten the legs and burn calories
- Short, effective workouts
Disadvantages:
- Can tire your legs quickly if you are unconditional
Comparison table
| machine | Impact level | Calories burned (30 minutes)* |
|---|---|---|
| treadmill | medium | 200–300 (walking/jogging) |
| Elliptical | Low | 240-300 |
| Stationary bike | Low | 210–250 |
| Rowing machine | medium | 250–350 |
| Staircase | medium | 300–400 |
*The burned calories depend on the user weight and intensity. (Source: Harvard Health, 2021)
Which cardio computer is right for you?
| Goal | Best option |
|---|---|
| Fat loss | Stair climber, rowing machine |
| Joint pain or recovery | Line bike, elliptical |
| Endurance building | Treadmill, upright bike |
| Strength and conditioning | Rowing machine |
| Total body activation | Elliptical, rower |
| Low effects and simple start | Inpatient bike, elliptical |
First steps: beginner -cardio routine
Example 20-minute cardio session:
- Warm up (3–5 min): Easy pace on the selected machine
- Main clip (15 min):
- 1 min moderate pace
- 1 min light (recovery)
- Repeat 7 rounds
- Cooling (2–3 min): Reduce intensity and stretch
Aim at 3–4 sessions per weekIncreasing duration and resistance gradually.
Last thoughts
When you start your fitness trip, you can choose the right cardio equipment to increase your trust, consistency and your results. Just start, listen to your body and concentrate on the right technology.
Consistence beats the intensity – make the machine that you enjoy the most and stay with it!
References
- Harvard Medical School. (2021). The calories were burned in 30 minutes for people with three different weights. https://www.health.harvard.edu
- American College of Sports Medicine (2021). ACSM guidelines for exercise tests and prescription (11th edition).
- Garber, CE, et al. (2011). Quantity and quality of the movement to develop and maintain cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults. Medicine & Science in Sports & Training, 43 (7): 1334–1359. https://doi.org/10.1249/ms.0b013e318213fefb
- Ainsworth, BE, et al. (2011). 2011 Compendium of physical activities: a second update of codes and fulfilled values. Medicine & Science in Sports & Training, 43 (8), 1575–1581.





