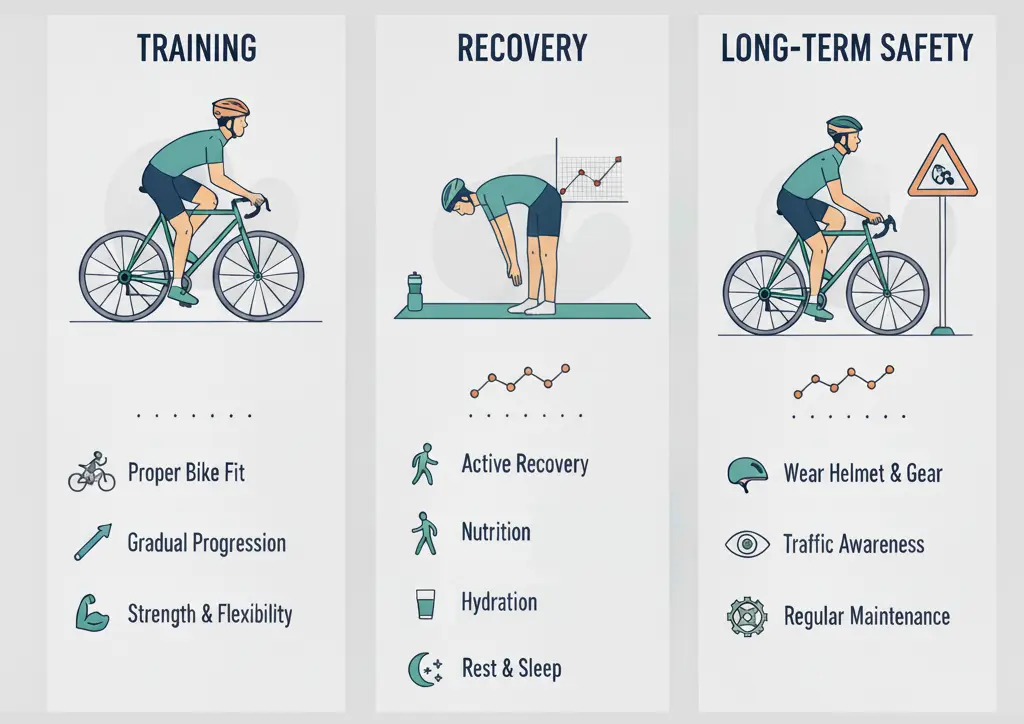
Cycling builds endurance, strengthens the lower body and delivers one of the best available training units with a low expression. But repeated movements and long hours in the saddle also demand tribute. From painful knees to tense back and sometimes more serious accidents on the street, injuries are an unfortunate reality for many drivers. The good news is that most bike injuries can be reduced or managed with intelligent training, deliberate recovery and safe driving habits.
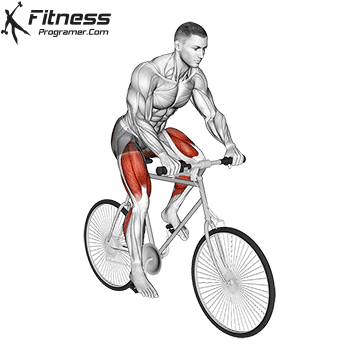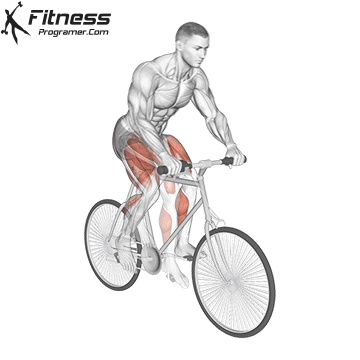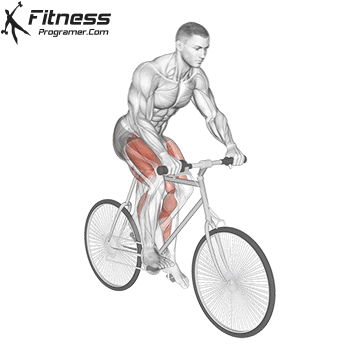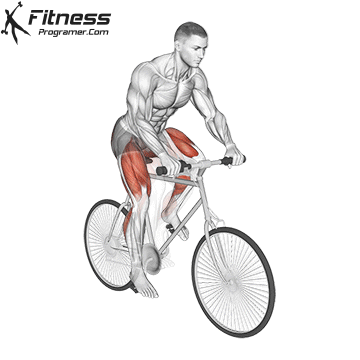
Why is injury prevention for cyclists important
Every pedal strike repeats the same movement in a single trip a thousand times. Over time, this repetition burdens the joints and supporting muscles. If the posture fails or there is no strength in key areas, small problems can quickly sum up. The most common problems are:
- Knee pain caused by improper saddle height, poor bicycle adjustment or weak support muscles in the joint.
- Discomfort of the lower back From poor posture, long hours in a crouching position or inadequate core stability.
- Neck and shoulder pollution Connected to the tension when you keep the handlebar too tight or lean too far forward.
Cycling also sets unique injury risks compared to other endurance sports. Runners often deal with injuries related to impact, while cyclists have more problems with overuse and attitude. Cycling represents different injury risks than other endurance sports, which means that prevention strategies are more tailored to the requirements of cycling and are not copied by other training programs.
Another factor is time in the saddle. Long-distance cyclists can travel by route for hours, and even leisure drivers can spend entire weekends by bike. Small inefficiencies, such as a slightly wrong route or a weak buttocks, can be enlarged over time and increase the likelihood of pain.
Ignoring these warning signs can lead to the development of chronic diseases. The patellofemoral pain syndrome (often referred to as the “knee of the cyclist”), sciatica and persistent neck slope are common examples of problems that start small but escalate if they do not remain adapted. As soon as these problems develop, you can set a cyclist for weeks or months pages and training progress and the fitness winnings.
For many drivers, injuries are not only painful; They interrupt training progress and limit the performance potential. Therefore, prevention is more than a secondary focus; It is a central part of a long -term cycling plan. If you stay healthy, a balance between conditioning, proper device furnishing and attentive training habits is required. If these elements are present, cyclists can consistently train, constantly build up endurance and spend more time to enjoy the journey.
Training to prevent injuries
The gym is one of the most effective places to build strength and mobility, protect cyclists on the go. A strong foundation reduces the wear on joints, improves the posture and makes the body more resistant to unexpected stress. The most important elements of a training plan for injuries include:
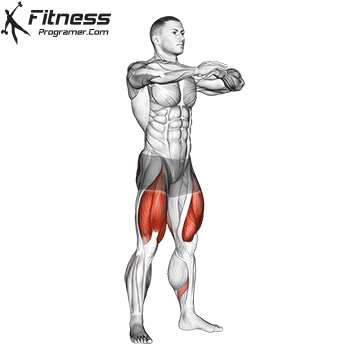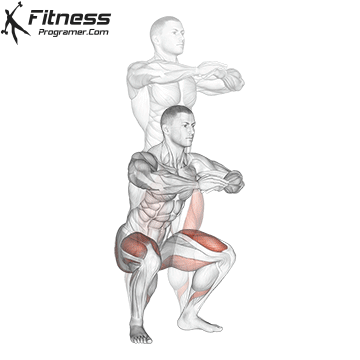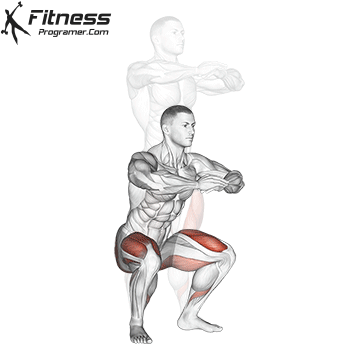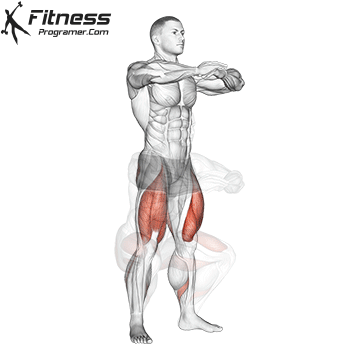
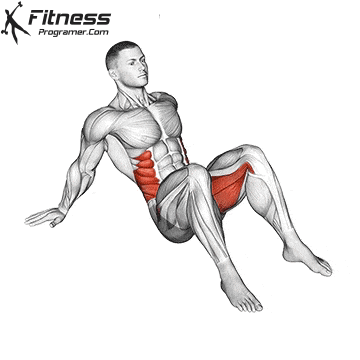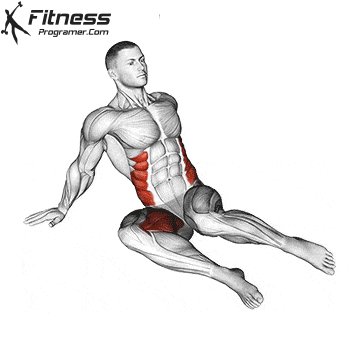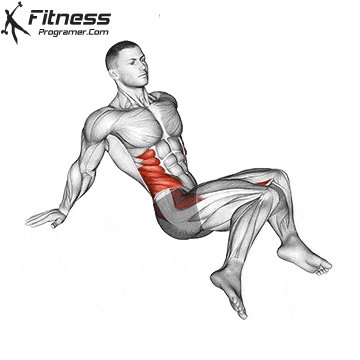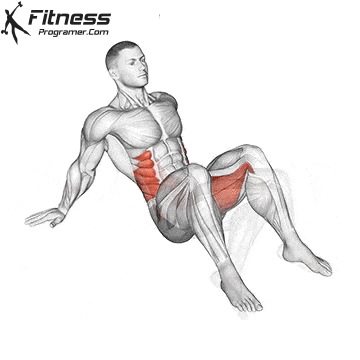
- Strength training: Exercises such as squats, lunge steps and hip bumps strengthen the gluteal muscles and the quadriceps that supply the pedal strike and protect the knees.
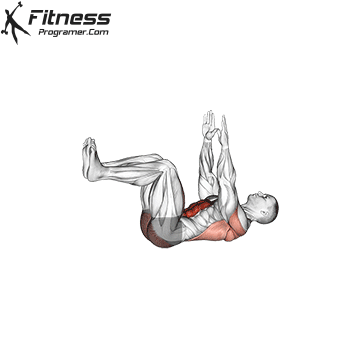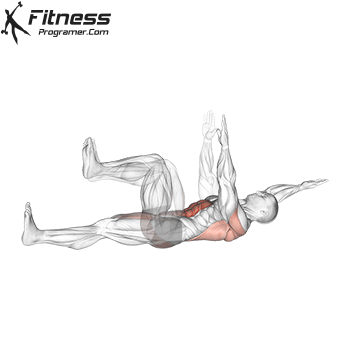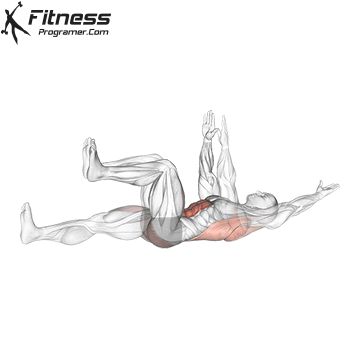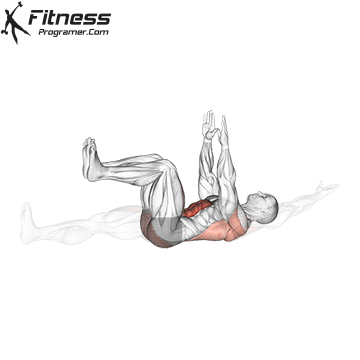
- Core stability: Boards, dead insects and rotation core work help to maintain the attitude on long journeys and relieve pressure from the lower back.
- Mobility work: Dynamic sections for the hips, knee tendons and shoulders improve flexibility and reduce the likelihood of violations of overlaps.
- Equilibrium training: One-leg exercises and stability ball drills improve control, especially when navigating through traffic or on uneven terrain.
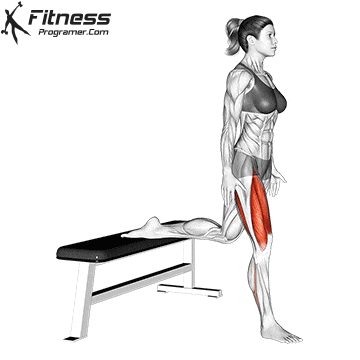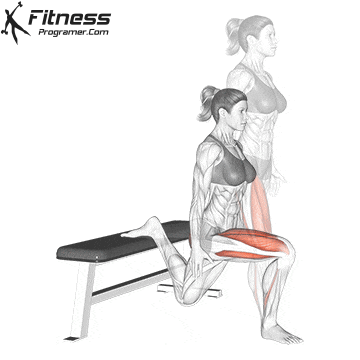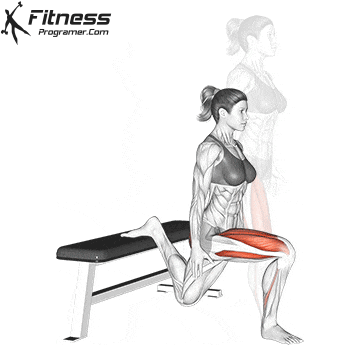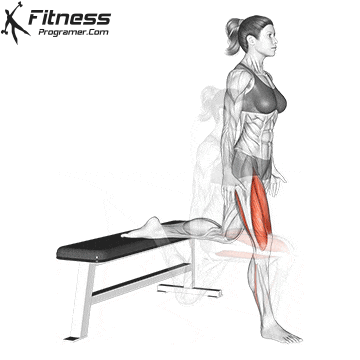
While training can reduce the likelihood of over -stress injuries, it cannot completely eliminate the risk. Location and driving conditions play an important role in bicycle security.
For example, Chicago has invested heavily in bike paths and cyclists. Dense traffic and hard winter conditions, however, still set a higher risk of accidents compared to cities such as Portland, Oregon, where protected alleys and milder weather create safe conditions. In contrast, auto-address regions such as Houston or Miami often report higher collision rates due to the limited cycling infrastructure.
These differences show how strongly the surroundings of a cyclist influence general security. In busy cities like Chicago, even well -conditioned athletes can be violated by accidents that cannot prevent them alone. Consult a in these situations Chicago bicycle accident lawyer Can provide valuable support and help drivers to concentrate on their recovery and at the same time ensure that their rights are protected.
Recovery strategies for cyclists
The recovery is the process through which the body adapts to the training and returns more. Without them, tiredness, performance drops and the risk of injury increases. An intelligent restoration plan consistently keeps cyclists, which is often more important than any individual training.
1. Active relaxation
On days between harder trips, the easy activity helps to loosen tight muscles and improve the circulation. Simple cycling, swimming or a short walk are enough to restore the movement without adding more stress.
2. Work and mobility work
Close hips, knee tendons and shoulders are common symptoms among cyclists. Dynamic routes before a trip prepare the body for movement, while static routes then help to maintain flexibility. By adding mobility roads for the spine and the hips, the load on the back is also reduced during long journeys.
3. nutritional value and liquid intake
The right fuel accelerates recovery. Protein supports the muscle repair, while carbohydrates fill up the energy consumed during cycling. Just as much hydrated affairs, since even a slight dehydration can slow down and increase the pain. After long or hot journeys, adding electrolytes helps to replace, which is lost by sweat.
4. Quiet and sleep
No restoration strategy works without sufficient calm. The repair of the muscles and hormones can bleach during deep sleep, which makes it one of the most effective tools to prevent injuries. The consistency here is of crucial importance, since late nights and irregular sleep can undermine the advantages of the best training program.
When you have to look for professional help
Pain that fades after a day or two is usually harmless; However, pain that refers or worsens require attention. Persistent symptoms in the knees, back or joints can indicate an injury that requires medical help. Evidence -based resources such as the Essential recreational strategies for young athletes The American College of Sports Medicine is highlighted if restoration routines are not sufficient and a professional evaluation is required.
Long-term bike safety tips
By preventing over -stress injuries in training and building a solid restoration routine, the basis for a consistent performance laid. However, cyclists must also take long -term security into account on the street and in their total driving habits. A balanced approach to preparation and consciousness reduces the risk both within and outside of training.
1. Bicycle adjustments and devices
A properly assembled bike is one of the best defenses against chronic pain. The adjustment of the saddle height, the handlebar position and the tunnel alignment ensure that the body moves efficiently and the tension of the joints minimizes. Investing in quality equipment such as padded shorts and well -fitting helmets also improves comfort and protection.
2. Road awareness
Even strong and experienced cyclists are susceptible to traffic dangers. Remaining with reflective clothing, using the correct lighting and following the traffic laws are non -negotiable security habits. Driving predictable and avoiding distractions such as headphones lowers the chances of collisions.
3 .. Training support
Supplementary exercises from the bike, including the routines for core strength and mobility, support a better attitude and a lower risk of injury on long journeys. For example, integrate Leg fluctuations (from front to back) Hip mobility improves in a warm -up routine and prepares the body for efficient pedals.
4th seasonal considerations
The weather significantly influences the driving conditions. Wet or icy roads require slower speeds and greater caution, while summer heat increases the need for moisture. Adjusting training and equipment for the season ensures security and consistency and effectiveness.
Diploma
Cycling brings the body through thousands of repetitive movements, which makes the prevention and recovery of injuries essential for long -term performance. Strength training and mobility work build up resistance, structured restoring routines prevent fatigue from turning into setbacks, and intelligent security habits reduce the risks in both training and on the street. By combining these strategies, cyclists can drive with greater consistency, self -confidence and protection against the challenges with sport.