What is ankle excavation?
Ankle expression occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle go beyond their borders or their tear. Bands are hard fabric tapes that stabilize joints. Sprovements occur frequently when the foot turns or rolls unexpectedly, causing the ankle joint to get out of its normal position.
What causes ankle expression?
Ankle intensification typically result from:
- Twist or roll the ankle: Often during sports or when walking on uneven surfaces.
- If: Waiting to land the ankle in an unnatural position.
- Sudden effects: Direct blows on the ankle can stretch or tear ligaments.
These incidents can rush or tear the ligaments, which leads to sprain.
What are the symptoms of ankle expression?
Common symptoms are:
- pain: Especially in the weight of the affected foot.
- swelling: Due to inflammation.
- Bruises: Discoloration around the ankle.
- Movement area: Difficulties to move the ankle.
- instability: Feeling of the ankle.
How is ankle -resuscitation diagnosed?
Diagnosis includes:
- Physical examination: Assessment of swelling, tenderness and movement area.
- Imaging tests: X -rays to exclude fractures; MRI or ultrasound for a detailed ligament rating.
Sorting the severity of the Spring auction
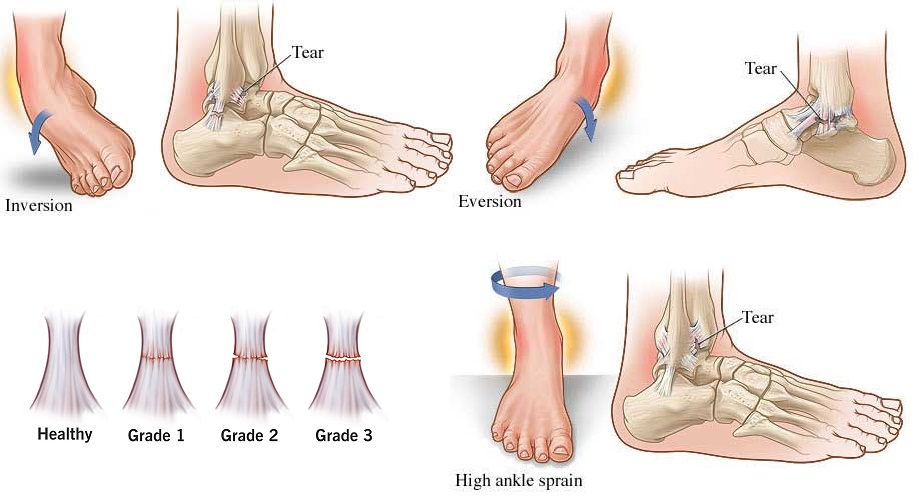
Ankle -immersion are usually divided into three classes based on the extent of the band damage. Understanding the severity of sprain is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan and the expected recovery period.
Sprain of grade I (mild)
- Band status: Overload without tearing.
- Common instability: Little to none.
- Pain and swelling: Light.
- Mobility effects: Minor difficulties when walking.
- Treatment: Conservative care such as calm, ice cream, compression and height (rice); Usually no long -term complications.
Sprain of grade II (moderate)
- Band status: Sometimes tearing of band fibers.
- Common instability: Mild to moderate.
- Pain and swelling: Medium -heavy to severity.
- Mobility effects: Some difficulties walking; There is often a slight bruise.
- Treatment: Can require a bracket or rail; Physiotherapy is often recommended for recovery and preventing the reinforcement.
Sprain III (serious)
- Band status: Full ribbon break.
- Common instability: Significant.
- Pain and swelling: Difficult.
- Mobility effects: Marked difficulty or inability to run due to intensive pain.
- Treatment: Requires a medical assessment; Immobilization, physiotherapy and in some cases may be a surgical intervention.
The Degrees/severity of an ankle inclination plays a crucial role in the design of the treatment approach. While mild cases can be managed frequently at home, heavier sprains from a doctor and/or rehabilitation support require medical support through a licensed physiotherapist.
What kind of sprain of ankle is?

The first care includes the RICE Procedure:
- Relax: Avoid activities that cause pain.
- Ice: Apply every 2-3 hours for 15-20 minutes of ice cream bag.
- compression: Use elastic bandages to reduce swelling.
- elevation: Keep your ankle over your heart.
Over-the-counter pain agents such as ibuprofen can help to manage pain and inflammation.
What are the risk factors for a sprain of ankle?
The risk factors include:
- Previous ankle injuries: Increases susceptibility to future sprains.
- Sports participation: Especially for sports that require jumping or quick changes in direction.
- Unequal surfaces: Go or run on irregular terrain.
- Inadequate shoes: Wearing shoes that do not offer proper support.
Frequently asked questions about ankle expression
Q: How long does it take for the ankle to recovered?
A: The recovery time varies. Light sprains can heal in a few days, while severe sprains can take several weeks to months.
Q: When should I see a doctor?
A: If you have severe pain, do not wear weight or consider a significant swelling or deformity, contact a health service provider.
Q: Can I prevent ankle excuses?
A: Yes. Strengthening exercises, proper shoes and careful on uneven surfaces can help prevent sprain.
References
- Breds ankle: symptoms, types, treatment and recovery. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/disases/22048-spraint-ankle
- Bredged ankle – symptoms and causes. Mayo clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/disasses-conditions/sprained-ankle/symptoms-causses/syc-20353225
- Bricked up ankle – orthoinfo – aaos. https://orthoinfo.aos.org/en/disases-conditions/sprained-ankle/
- Sprain of ankle and expansion risk sports health. https://www.sports-health.com/sport-injuries/ankle-and-foot-injuries/ankle-sprain-and-strain-risk-factors





