The EZ Curl Bar, known for its angled grip design, has become an integral part of many gyms, both commercial and at home. Despite its widespread use, some lifter and fitness experts still ask whether the EZ Bar Curl is really advantageous for the construction of biceps.
To remedy this, we have to see the unique mechanics of the EZ beam, how to activate the muscles and how to stack against other biceps exercises such as straight beams and Dumbbell curls. We will also see his potential Common health benefitsHis role in hypertrophy Programming and whether it is a must or a nice tool for arm training.
What is the EZ Bar Curl?
The EZ -Bar Curl is a biceps insulation exercise with an EZ -curl rod, a short barbell with angled handles. These handles let their hands take one half -suped or neutral-summined Position. The angles of the handles reduce the wrist and forearm rotation, which usually leads to fewer wrists and elbows compared to a straight beam.
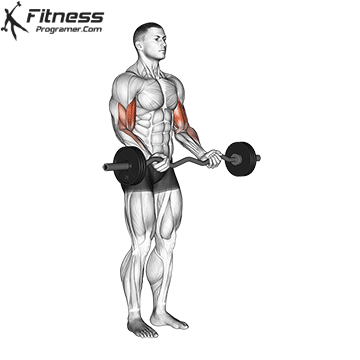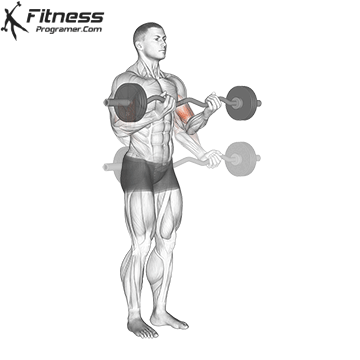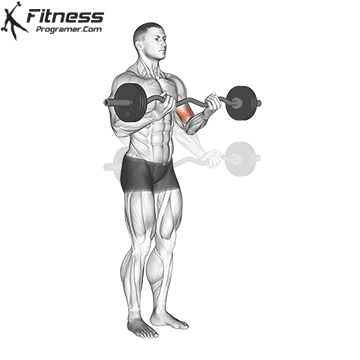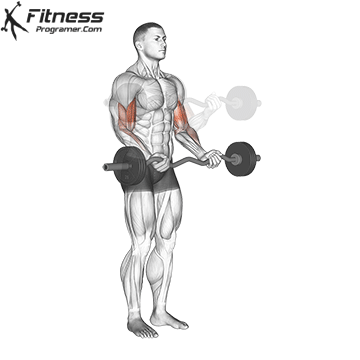
Lifter conduct the movement similar to a traditional curl: the rod begins at arm length and is lifted through the elbow flexion until the forearms are vertical or light. The rod is then lowered again under control to the starting position.
EZ Bar Curl vs. Straight Bar Curl: Key differences
| Specialty | EZ bar curl | Just bar curl |
|---|---|---|
| Grip position | Angled / half -suped | Fully suined |
| Wrist stress | Reduced | Increased (especially for people with mobility problems) |
| Forearm activation | Moderate | Higher (due to rotation requirements) |
| comfort | Larger, especially for elbow/wrist complaints | Can make existing common problems worse |
| Load tolerance | High (but usually less than just beams) | High |
| Short head focus | Slightly reduced (due to less supination) | Possibly greater |
Both variations commit them Biceps BrachiiBut the EZ beam could easily reduce activation of the activation short head Because of its less extreme supination.
However, the Comfort and stability The liver offered by the EZ CURL bar often enable lifts to work harder, longer and more often, especially if common symptoms would restrict the performance with a straight beam.
Muscle activation: What does research say?
EMG studies for comparison of CURL variations suggest that:
- The Biceps Brachii the primary mover remains in all variations, including EZ -Balken curls.
- EZ sticks tend to reduce the peak easily Short head biceps Activation compared to fully supined handles.
- However, the Brachioradialis And Brachial Show an increased or similar activation with the EZ handle, which makes it a rounded bracket.
These results imply that the EZ -Balken -Curl may not be aimed at the biceps with maximum top activation compared to a strict supinated curls that affects other elbow flexors more conveniently and more Joint -friendly load-of particular useful during the band-based hypertrophy training.
Common health and comfort: a great advantage
One of the most frequently cited advantages of the EZ -Bar is the ability to Reduce the load on the wrists and elbowswhich are often vulnerable to the repeating curling with straight beams. The angled handle shifts the forearm into a more neutral position and minimizes the outer rotation on the shoulder and torsion on the wrist. This makes it an excellent option for people who experience:
- Golfers Ellbogen (media epicondylitis)
- Wrist tendon complaints
- Limited forearm -ups or shoulder mobility
For this reason alone, many trainers recommend the EZ Bar Curl as A Long -term staples In arm training routines, even if it is not always the biomechanically “pure” biceps insulation movement.
Is the EZ -Bar Curl effective for hypertrophy?
Yes. Despite a slight compromise in supination, the EZ -Bar Curl remains very effective for the construction of both Biceps size And Total criminal mass For the following reasons:
- It enables you to train more heavily without affecting common comfort.
- You can collect more training volume Over time with less fatigue.
- You recruit muscles supportive Like the brachial and brachioradialis that contributed to the thickness of the upper arm.
- It is well suited for Intensity techniques As with drop sets, tempo curls and mechanical advantage.
In the programming Dumbbell curls and hammer variations, EZ-Bar curls significantly contribute to a rounded ARM development program.
Program the EZ -Bar Curl in your training
The EZ -Bar -BARR -BARK can be used effectively in several training contexts:
- As the main stronger builder With heavier sentences of 6–8 repetitions
- As a volume driver With moderate weight in the 10–15 Rep area
- As part of super sets or circuitsalternating with shoulder or triceps work
- As a relaxing alternative During Deloads or when returning elbows/wrist problems
Example hypertrophy superset:
- EZ bar curl – 3 × 10–12
- Silent dumbbell curl – 3 × 12–15
(Rest 60–90 seconds between super sets)
To avoid frequent errors
- The bar swing Or use with impulse instead of a strict elbow flexion
- Do not extend the bottomReduction of the area of movement
- Use an excessive narrow or wide gripWhat the wrists can strain
- Lean back To raise heavier weights and strain the lower back
Form is critical with the EZ -Bar Curl. Even if it is a common friendly, excessive stress or bad technology, this can lead to suboptimal recruitment or injury.
Conclusion: Is the EZ Bar Curl worth?
Yes – the EZ Bar Curl is absolutely worth involving your training routine, especially if you appreciate Long -term common healthPresent Progressive overloadAnd Training consistency. While biceps have not insulated the biceps as well as some other variations, its ability to reduce symptoms and to facilitate the progression of the load makes an excellent tool for hypertrophic athletes.
Instead of asking whether the EZ -Bar is better or worse than others, the more effective strategy is to integrate it into A balanced arm routine This includes stick curls, dumbbell curls and hammer -cathers. This approach ensures that all heads of the biceps and the surrounding elbow flexors are effectively trained, which promotes maximum arm development over time.
References
- Signorile JF, et al. (2002). Electromyographic analysis of muscle activity in conventional and modified dumbbells. J Strength Cond Res.
- Schoenfeld Bj. (2010). The mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application to strength training. J Strength Cond Res.
- Oliveira LF, et al. (2009). EMG analysis of Biceps Brachii in various curling exercises. J Sports sci med.
- Saeter bakken ah et al. (2020). Effects of different biceps curl on muscle activation and power performance. Peerj.
- Boeckh-Behrens Wu, et al. (2003). Biomechanical analysis of the forearm position in biceps -curl variations. German Journal of Sports Medicine.





